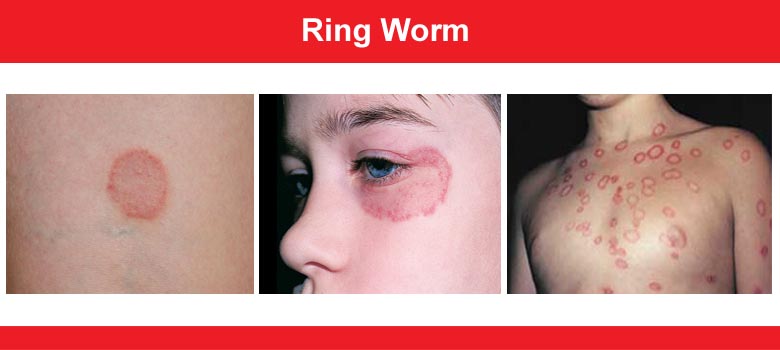
Ringworm is a common skin infection that is caused by a fungus. It’s called “ringworm” because it can cause a circular rash (shaped like a ring) that is usually red and itchy. Anyone can get ringworm. The fungi that cause this infection can live on skin, surfaces, and on household items such as clothing, towels, and bedding.
Causes of ringworm
Ringworm is caused by a fungus that grows on the skin. Once the fungus is established, it spreads out in rings. The centre of the ring may clear up, while a new ring of infection develops at the edge of the old ring. Children are most likely to get ringworm. Ringworm of the scalp can spread from child to child when children share hats, combs, or brushes. Ringworm of the body can be spread on towels, clothing, or sports equipment. Personal hygiene is important in preventing the spread of ringworm.
The following are the different types of ringworm
Tinea barbae
Ringworm of the bearded area of the face and neck, with swelling and marked crusting, is often accompanied by itching, sometimes causing the hair to break off. In the days when men went to the barber daily for a shave, tinea barbae was called barber's itch.
Tinea capitis
Ringworm of the scalp commonly affects children, mostly in late childhood or adolescence. This condition may spread in schools. Tinea capitis appears as scalp scaling that is associated with bald spots (in contrast to seborrhea or dandruff, for instance, which do not cause hair loss).
Tinea corporis
When fungus affects the skin of the body, it often produces the round spots of classic ringworm.
Tinea cruris
Tinea of the groin ("jock itch") tends to have a reddish-brown color and extends from the folds of the groin down onto one or both thighs.
Tinea faciei (faciale)
ringworm on the face except in the area of the beard. On the face, ringworm is rarely ring shaped. Characteristically, it causes red scaly patches with indistinct edges.
Tinea manus
ringworm involving the hands, particularly the palms and the spaces between the fingers. It typically causes thickening (hyperkeratosis) of these areas, often on only one hand. Tinea manus is a common companion of tinea pedis (ringworm of the feet). It is also called tinea manuum.
Tinea pedis
Athlete's foot may cause scaling and inflammation with itching and burning irritation in the toe webs, especially the one between the fourth and fifth toes. Another common form of tinea pedis produces a thickening or scaling of the skin on the heels and soles.
Tinea unguium
Finally, fungal infection can make the fingernails and, more often, the toenails yellow, thick, and crumbly. This is referred to as fungal nails or onychomycosis.
Treatment for ringworm
Homeopathy and ayurveda are effective for chronic Ringworm.
Our treatment based on homeo and herbal medicines addresses altered immune system, treating the roots of the disease.It is not superficial but deep acting; gives lasting to almost permanent results in most cases.It is absolutely harmless, safe and non-toxic.

